What Is A Motherboard VRM? Why Is It Important.
The Voltage Regulatory Module (VRM) part within the motherboard steps down the uncooked 12 V energy provide to 1.2 to 1.45 V required by the processor, RAM, and different elements.
While this isn’t the very first thing that pops up in our thoughts when selecting a motherboard, it’s nonetheless important, particularly for overclockers.
If you’re searching for increased clock speeds, know that it requires clear and steady voltage, which is simply potential with high-quality VRMs.
If your motherboard consists of a low quantity or poor-quality VRMs, it could actually considerably influence its lifespan.
It could mess up the ability supply and even result in frequent crashing, blue display errors, and everlasting injury to your PC elements.
Buckle up as I’m going to debate all the things it is best to find out about motherboard VRMs on this in-depth information.
Motherboard VRM Constituents
Let me clear this confusion immediately – the 12 V equipped by the PSU doesn’t straight attain the processor.
It passes via diodes and resistors earlier than touchdown on the VRM, the place the present is stabilized and voltage is stepped down as per the CPU’s requirement.
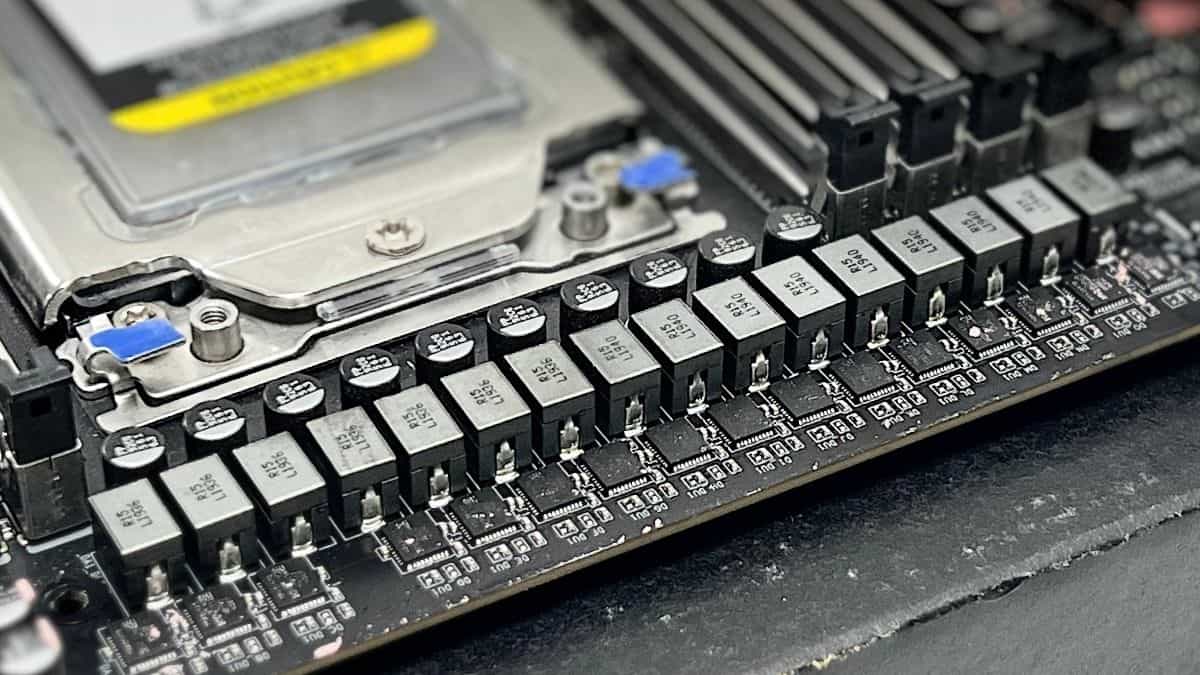
The Voltage Regulatory Module consists of a number of MOSFETs, chokes, and capacitors. Each of them has a selected operate and is important for correct/clear energy supply.
These elements are nicely scattered across the processor socket. Without them, your CPU would fry out. That mentioned, listed below are some basic items it is best to know.
MOSFETs
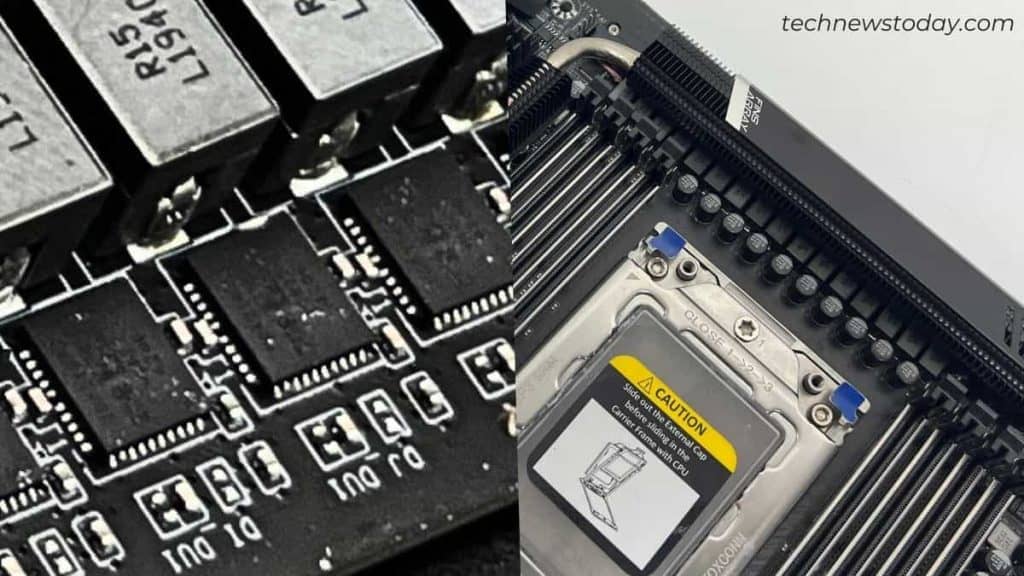

As the identify suggests, the metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors are liable for opening and shutting the digital gates. This means the inductors/chokes are charged solely when the change is closed.
These transistors sit beneath the VRM heatsink. So, it’s fairly simple to guess that these elements are those that produce probably the most warmth. That’s just because a MOSFET has to open and shut 1000’s of occasions per second.
While they’re designed to resist temperatures as much as 150 levels, they are going to finally die if overheated. That’s the explanation most boards include a devoted sensor so you’ll be able to examine the MOSFET temperature infrequently.
In the previous, motherboards used to return with a set of MOSFET chips – excessive and low aspect switches. But in fashionable fashions, you’ll solely discover a single transistor that accommodates the performance of each.
Chokes

These are magnetic inductors that sit next to the MOSFETs, exterior the heatsink. Chokes are a lot simpler to identify on older methods as you’ll be able to see the giant coils fairly clearly.
On the opposite hand, the motherboard that we personal right this moment has a square-shaped blocky design, and the coils are safeguarded there.
When the circuit is closed, the inductors begin to get charged. At this second, the electrical vitality is transformed to the magnetic area and your CPU will get ample energy. More on this later.
Capacitors
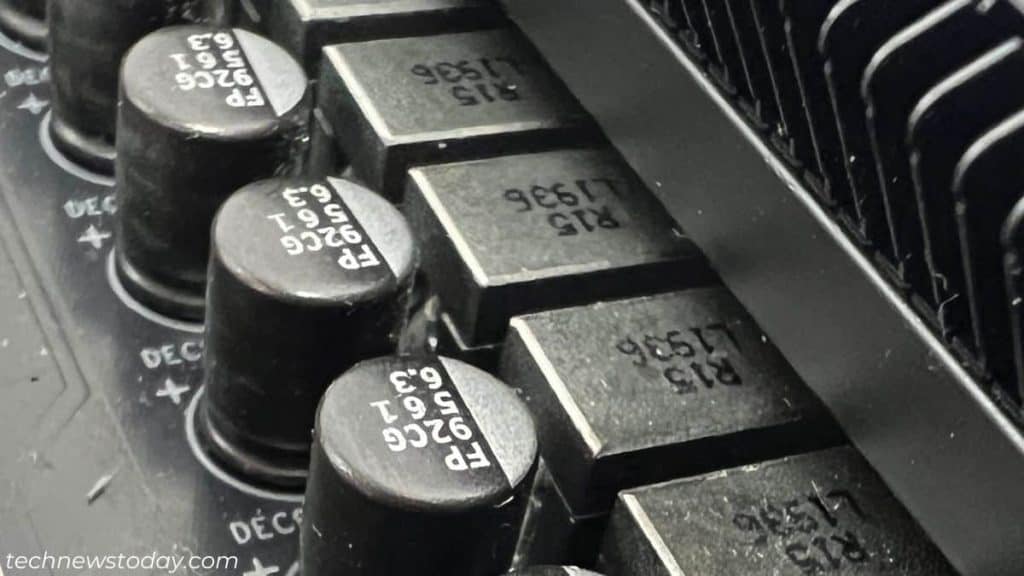

As with some other digital device, even motherboards are outfitted with a considerable amount of capacitors. These cylindrical-shaped our bodies have an working restrict and life expectancy.
For instance, in some motherboards, capacitors are rated to function on the most temperature of 105 °C.
So, if the motherboard temperature goes past the restrict (particularly as a result of voltage spikes), they might bulge and even pop.
Usually, motherboards designed for higher overclocking include high-quality solid-state capacitors.
Avoid a budget ones which have conducting liquids and have a better likelihood of rupturing, thus rendering the motherboard ineffective.
Capacitors are supposed to right the voltage ripple and spikes. They act as batteries that retailer the extra electrical energy (normally, in a small quantity), and convert it into steady and constant voltage.
PWM Controller
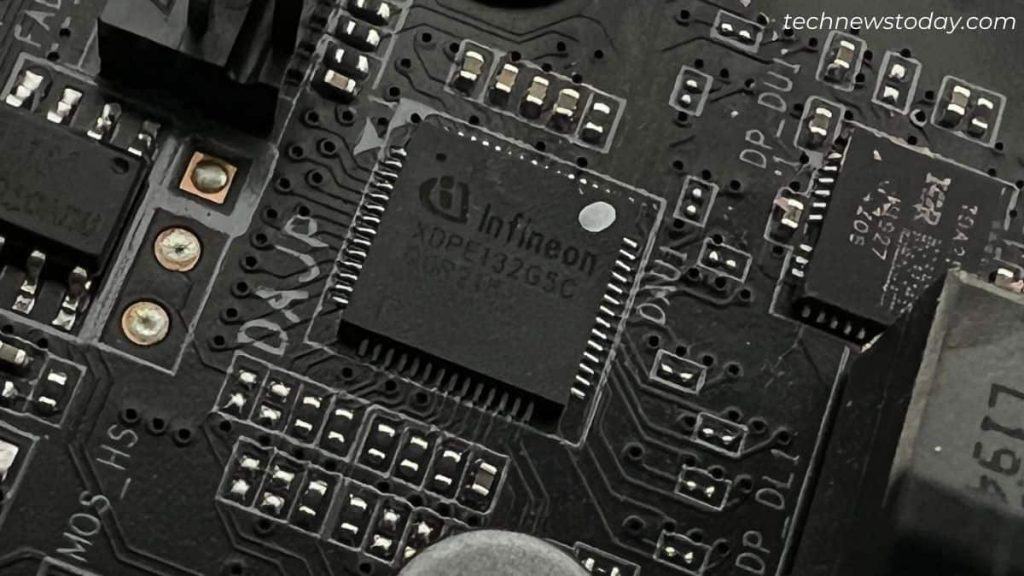

This is the grasp management chip of the VRM because it instructs all of the core elements (MOSFETs, chokes, and capacitors) for the correct functioning via pulse alerts.
In the previous, the PWM controller on a majority of motherboards used analog alerts. The newer boards now make the most of digital PWMs, however that doesn’t imply the analog ones are utterly outdated.
This element can also be liable for monitoring and regulating voltage, taking the VREF (Voltage Reference) accessible within the BIOS settings.
There won’t at all times be a PWM indication on the devoted chip. For instance, my TRX40 AORUS MASTER labels it as DAU1.
Likewise, some boards include a Dr MOS chip, which works using exterior pulse-width modulation.
Working of the Voltage Regulatory Module
Now that you’ve the final idea of every VRM element, let’s see how the buck converter works to step down voltage and distribute energy effectively. I’ll use bullet factors to make this simpler to grasp:
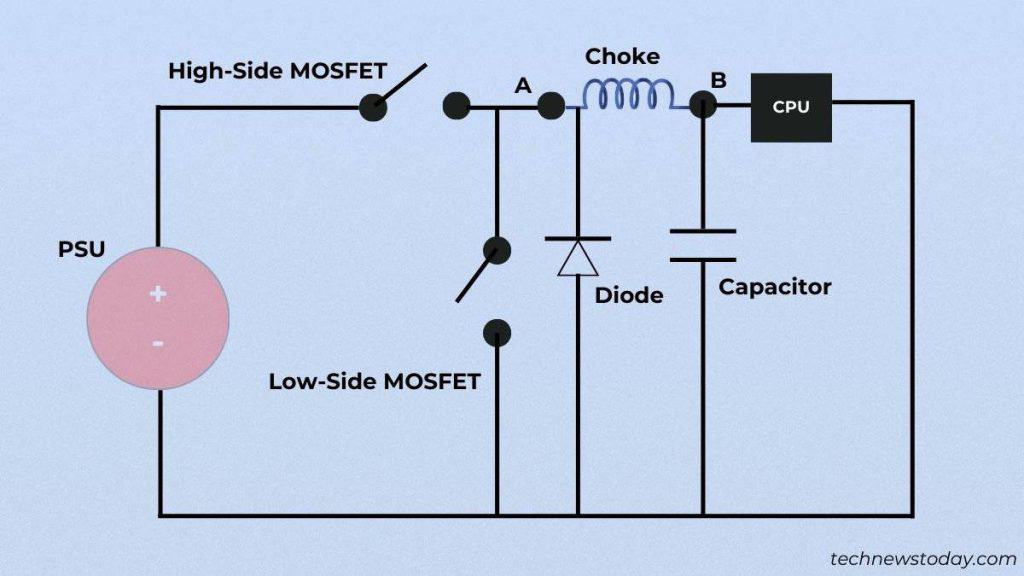
- First, the uncooked voltage (12 V) reaches the MOSFET.
- The main or high-side change closes the circuit. This means the electrical energy is now handed to the choke.
- Here, the equipped energy is filtered, and the coils are charged. Once the inductor absolutely prices, its output could have the identical voltage because the enter. And the vitality is saved in a magnetic area.
- It’s the PWM Controller that instructs the choke to discharge the correct quantity of voltage (1.2 to 1.5 V) to the CPU. This lasts so long as the circuit stays closed. The identical goes for RAM (1.2 to 1.4 V).
- As quickly because the circuit is open, the voltage begins to drop. But remember that when the high-side change is open, the low-side stays closed, and vice versa. If each open, the magnetic area could collapse, damaging the CPU’s life completely. This completes the primary spherical.
- Since the CPU will take a considerable amount of energy, the choke could lack electrical energy for the subsequent spherical. That’s when capacitors come into play, which have been storing small quantities of prices within the earlier steps.
- The identical vitality is used to cost the inductors and that is how the CPU/RAM receives clear and constant voltage.
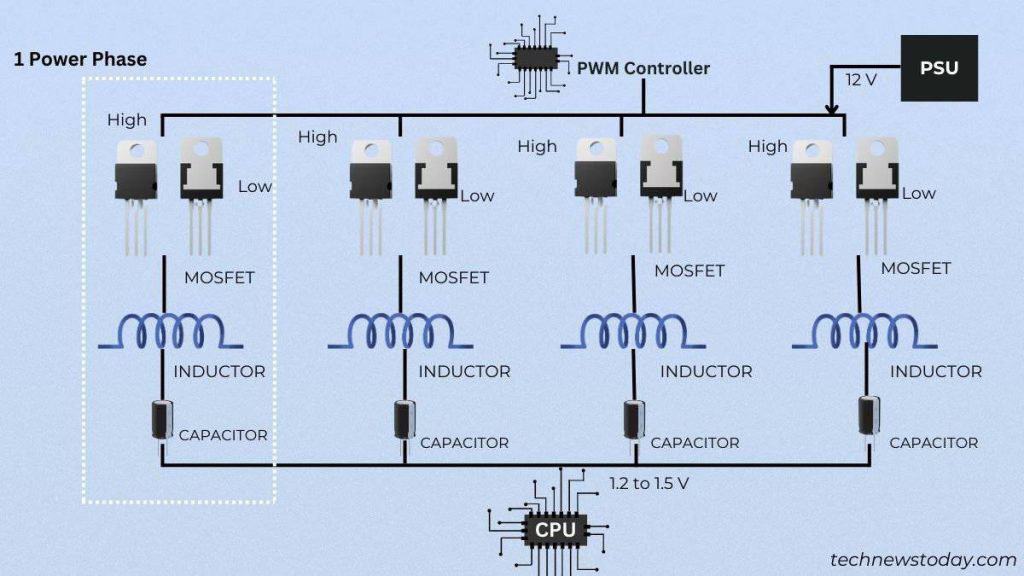
- To present more steady energy, a number of such circuits are linked. This is what we name a multiphase VRM.
What Exactly Are Power Phases?
Don’t get so confused by the time period ‘power phase’. You have already mastered this you probably have correctly understood the earlier rationalization.
Just know that the mixture of a MOSFET, choke, and capacitor forms one part. Similarly, one other set of the desired VRM elements forms the second part, and so forth.
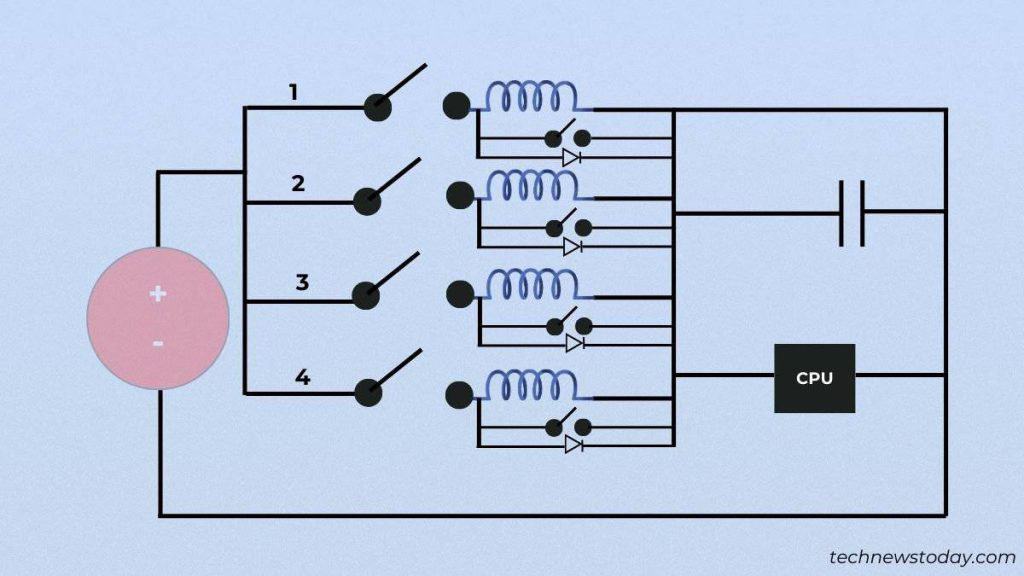
For instance, if a CPU requires 80 A present to function, all of it’ll move via one circuit in single-phase VRMs. But in case your motherboard has 4 phases, every circuit will deal with 20 A present.
The more the variety of phases, the higher the ability is cut up. The course of even results in a excessive variety of ‘switching losses’, which might be managed via a number of phases.
That additionally requires a multi-phase PWM for higher voltage regulation. Meaning, one PWM controller is devoted to at least one VRM part.
For higher overclocking help, high-end motherboards are all outfitted with more energy phases. Also, they arrive with higher cooling via top-quality heatsinks.
If you need to determine the variety of energy phases in your system board, this may be merely completed via bodily inspection. Counting the variety of chokes ought to be sufficient.
Inspecting the variety of capacitors and MOSFETs isn’t the suitable strategy although. That’s as a result of some boards undertake the phase-extend topology (the place VRM doublers are used).
We could have an in depth information on Twin and Phase-Extend VRMs quickly. For now, simply take a peek on the illustration beneath:
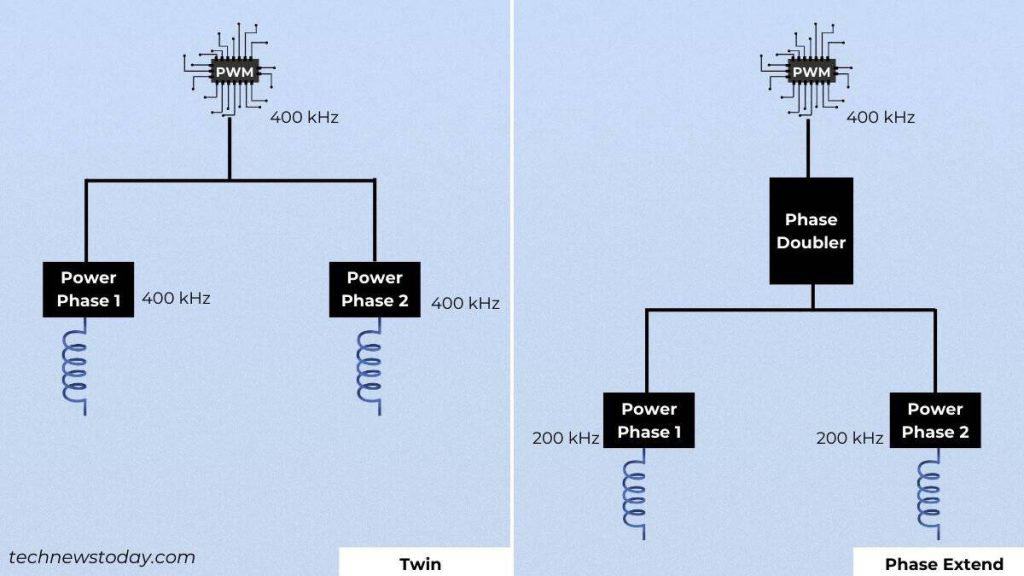
Here, the inclusion of a part doubler splits the frequency coming from the PWM controller. But the one and not using a doubler will ship the identical sign (with none delay) to each phases.
Understanding VRM Specs When Choosing a Motherboard
When inspecting the motherboard specs, most individuals overlook the significance of VRM. In reality, some boards (together with my MSI B550M MORTAR) don’t embrace something about such.
Gigabyte boards typically designate the VRM specs in X+Y format. For instance, my TRX40 AORUS MASTER has 16+3 energy phases. Here, 16 is for the CPU and three for RAM.
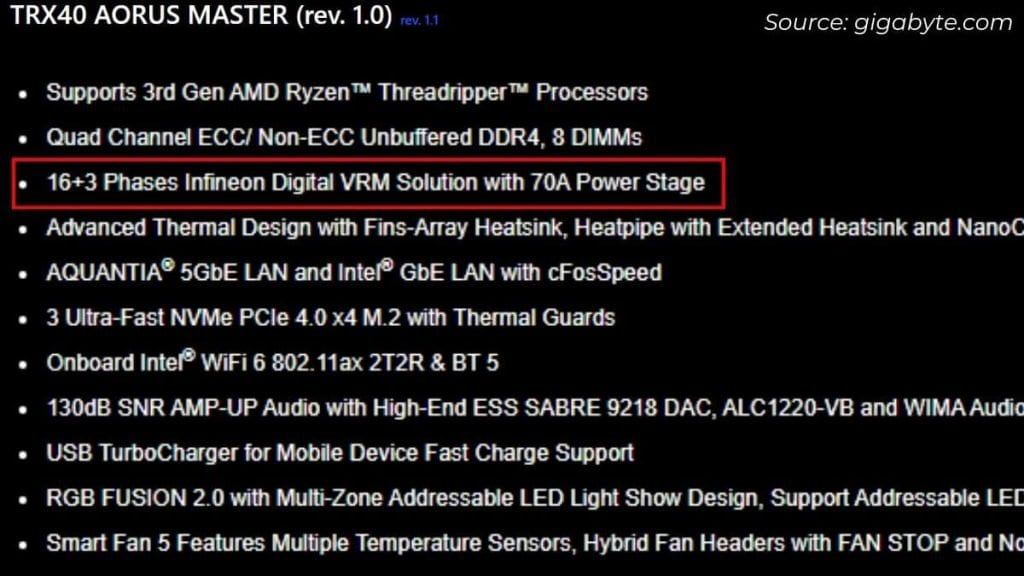
Also, it’s value noting the ‘70 A power stage’, which merely means the motherboard can provide 70 A present to the processor. And as defined earlier, with 16 energy phases for the CPU, every part handles 4.375 A.
Some older boards would possibly present this within the X+Y+Z format. X is normally for the processor, whereas Y and Z are for different elements, one among which is for reminiscence.
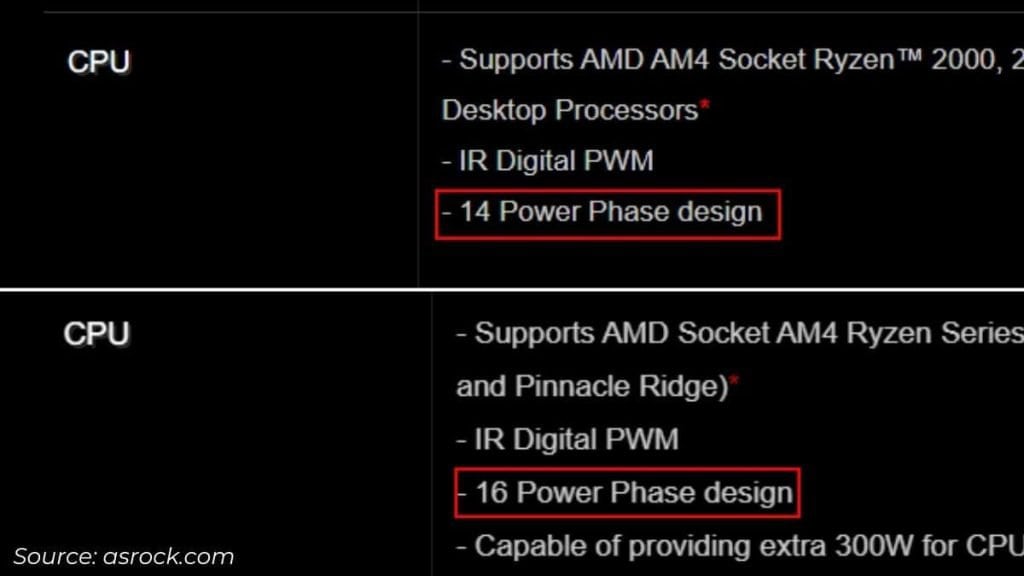
Most ASRock computer systems that we personal solely point out the overall variety of energy phases. For instance, X570 AQUA has a complete of 14 whereas X370 Taichi has 16.
However, it doesn’t specify the precise quantity for CPU and RAM. So, I recommend counting the variety of chokes to seek out this out your self.
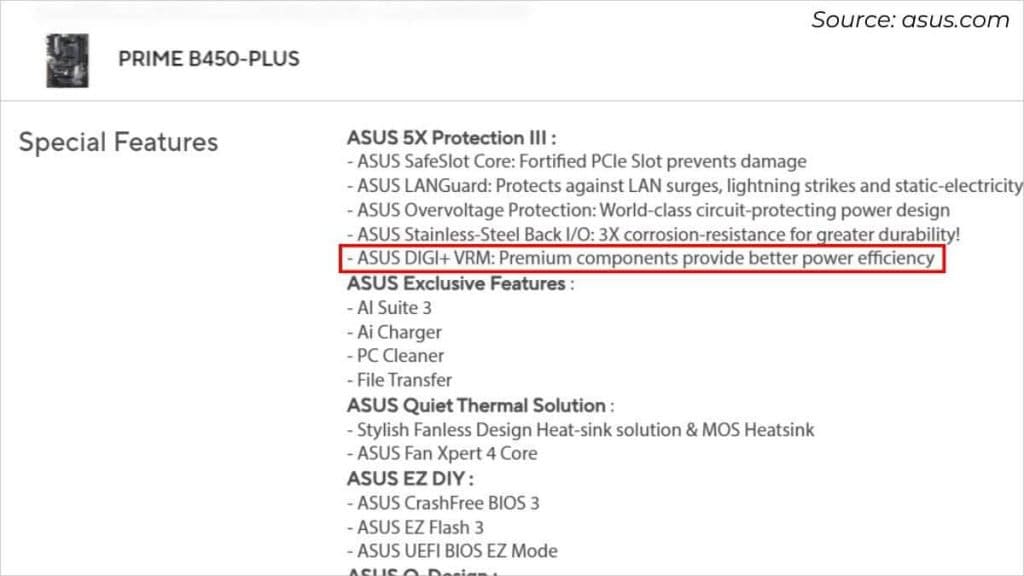
What I’ve observed on fashionable ASUS boards is most include DIGI+ VRM. Well, it merely refers back to the digital voltage regulator, which is much better by way of energy stability and overclocking in comparison with analog.
You see, each motherboard is totally different, and the variety of energy phases together with topology is exclusive. But now that you just’re conscious of most stuff associated to VRM, this shouldn’t be an element to fret about.
Kindly notice that your motherboard VRM isn’t the one factor that offers with energy supply. When constructing a PC, you also needs to select a PSU with top-notch high quality and with good effectivity.
Check out more article on – How-To tutorial and latest highlights on – Technical News








Leave a Reply