Thermal Paste Vs Liquid Metal—Which One Is Better.
Thermal paste primarily is available in two variants — commonplace thermal pastes that use a base matrix (like silicon-based) and liquid-metal-based ones.
PC lovers reward liquid steel because the best Thermal Interface Material (TIM) for cooling. Some customers have even claimed that it drops the temperature by whooping 10°C or more.
However, it’s fairly dangerous to use liquid steel paste with out correct precautions and expertise. So, relying in your scenario, it might be higher to make use of different common thermal pastes as an alternative.
What is Thermal Paste?

Standard thermal pastes use a base matrix along with a thermally conductive filler to supply a fluid pasty consistency. Most widespread thermal compounds are silicon-based.
But you’ll additionally discover carbon-based, ceramic-based, diamond-carbon-based, and metal-based compounds in the marketplace.
The matrix often comprises silicones, acrylates, urethanes, and epoxies, that are thermal insulators. The paste has to depend on the fillers that make up 70-80% of its composition to supply thermal conductivity.
These fillers are both one or a few — aluminum oxide, zinc oxide, boron nitride, aluminum nitride, and carbon micro-particles. Depending on the kind of the thermal paste, it might include further substances like silver and aluminum mud (metal-based), diamond powder (diamond carbon-based), and so forth.
What is Liquid Metal?
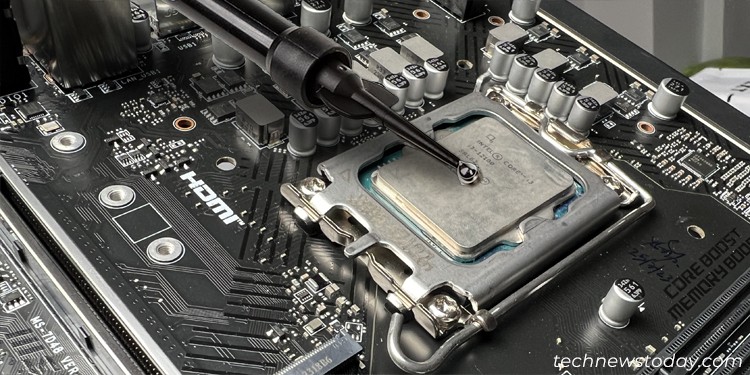
Unlike the common thermal pastes I’ve mentioned above, liquid steel instantly makes use of steel that stays liquid at room temperature as an alternative of counting on a base matrix.
The steel is often an alloy of gallium, indium, and tin, the place the gallium is the principle element.
Since all of the thermal interface materials is a steel, it has a lot greater thermal conductivity than different varieties of thermal paste and permits higher dissipation of warmth to the cooler.
This thermal interface materials is very most well-liked by PC lovers who wish to overclock their CPU and need the bottom doable temperature for his or her CPU.
Differences Between Thermal Paste and Liquid Metal
While commonplace thermal pastes and liquid metals have the identical working mechanism, their composition brings about sure variations that make them stand other than each other.
Heat Transfer/Dissipation and Cooling
While determining how good of a cooling resolution liquid steel or different thermal pastes make, we have to take into account their thermal conductivity. The greater the thermal conductivity, the higher it will possibly dissipate warmth and keep an efficient cooling system.
Both varieties of thermal interface materials can’t maintain a candle to that of the warmth sink (Aluminum – 237 W/m.Ok, Copper – 400 W/m.Ok) on this regard. However, it’s higher to make use of an interface materials with as excessive a dissipation price as doable.
The thermal conductivity of standard thermal paste’s base matrix is about 0.17-0.3 W/m.Ok. Depending on the filler materials, the whole thermal conductivity of the silicon or carbon-based paste often will get raised to 0.5 – 4 W/m.Ok.

Some high-end thermal pastes like silver-based or diamond carbon-based ones can have thermal conductivity starting from 3-8 W/m.Ok. According to ARCTIC, any values greater than this are doubtless mere gildings.
For liquid metals, the thermal conductivity can transcend 13 W/m.Ok. The primary substance in most liquid metals is Gallium, which has a thermal conductivity of 33.68 W/m.Ok.
However, it’s usually used as an alloy with Indium and Tin, and the liquid steel’s paste usually ranges from 17-40 W/m.Ok.
Many high-end liquid steel TIM producers additionally promote products claiming a thermal conductivity of 70-80 W/m.Ok.
Drying
Standard thermal pastes use solvents to carry all of the filler with a pasty consistency. With common publicity to excessive warmth, these solvents regularly evaporate, inflicting the paste to dry out.
Liquid metals don’t want to make use of such solvents, in order that they don’t dry out or present any degradation over time.
Corrosion
While the liquid steel doesn’t dry out over time, its primary materials, Gallium, may be very reactive and may corrode different supplies. You will particularly see this problem with Aluminum base or warmth sinks on the cooler.
So, it is best to solely use liquid steel with appropriate coolers which have copper or nickel-plated base.
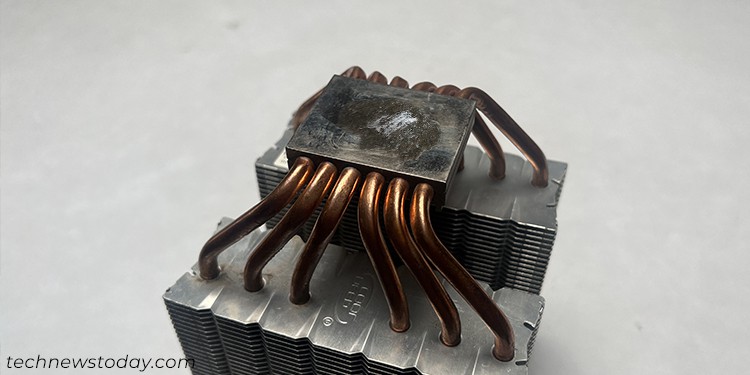
Even with copper/nickel, it will possibly create an alloy that results in discolorations within the base plate. It occurs over time, particularly because of the fixed publicity to warmth. But it received’t have an effect on the warmth trade course of a lot, so you possibly can relaxation assured.
Regardless, I personally suggest using coolers with nickel-plated bases if you wish to use liquid steel, as it’s the slowest at forming the alloy.
As far as different thermal pastes are involved, they don’t include any such corrosive parts.
Electrical Conductivity
Apart from corrosion, you additionally want to fret concerning the electrical conductivity of the thermal interface materials.
Most thermal pastes (silicon, carbon, diamond carbon, or ceramic-based) usually are not electrically conductive. So using them received’t trigger any quick circuit points in the event that they leak into digital circuit parts.
Thermal pastes which have steel fillers could be electrically conductive, and it’s essential watch out to not spill it into any circuit components. It’s additionally higher to make use of electrical tape on close by parts to account for sudden leaks.
As for liquid metals, consider them as metal-based thermal paste however worse. They are far more electrically conductive and may trigger extreme injury as a consequence of quick circuits in the event that they ever leak to different PC parts.
Cost
The excessive thermal effectivity of liquid metals instantly corresponds to their value. Depending on the standard of the liquid steel TIM, it will possibly value wherever between $10 and $20 per gram.
For different varieties of thermal paste, you possibly can often purchase them at about $1 – $4 per gram. Diamond-carbon-based thermal pastes will value barely more however not as a lot as liquid steel.
On the flip aspect, it’s essential use a low quantity of liquid steel each time, and also you don’t have to interchange it as a lot as common thermal paste, so it received’t be as costly in the long term.
Ease of Application

Since liquid steel can hurt the PC parts, it’s essential be very cautious whereas making use of it. You want to use a really skinny layer of the liquid steel evenly using a spreader whereas avoiding spills or leaks.
Just using a sample or depositing it within the center as with commonplace thermal pastes, just isn’t advisable for this TIM.
Also, whereas neither common thermal paste nor liquid steel are poisonous, they’ll trigger slight hurt to the human physique. In this regard, liquid steel is more dangerous, and it’s essential be much more cautious whereas dealing with it in order that it doesn’t get to your eyes otherwise you don’t inhale any fumes.
It’s higher to be in a well-ventilated room and use gloves and a protecting eye masks.
Which Thermal Interface Material Should I Use?
If you may have prior expertise in using liquid steel or can get assist from such an individual, and you’re going to push your CPU to its limits, you possibly can set up it so long as you don’t use any coolers with aluminum base.
Otherwise, commonplace thermal pastes needs to be greater than sufficient in your use. Unless you’re overclocking your PC or have a really heavy workload, the CPU temperature distinction wouldn’t be that prime in comparison with liquid metals.
If you’re on the lookout for a high-end resolution, diamond carbon-based ones ought to present superb thermal dissipation with out introducing any dangers that include liquid metals.
If you actually wish to use liquid steel, be certain to make use of electrical tapes on all close by parts and across the CPU to stop injury as a consequence of leaks. Also, remember the fact that making use of liquid steel leaves a conspicuous mark on the heatsink, so that you run the chance of voiding your guarantee.
Check out more article on – How-To tutorial and latest highlights on – Gaming News





Leave a Reply